One Simple Step to Help You Lose Weight and Balance Blood Sugar
Research published in the British Journal of Nutrition makes a strong case that a plate full of vegetables can help you lose weight.
Researchers at Japan Women’s University in Tokyo, Japan, asked volunteers to eat four different meals in a random order on separate days.
They found that the addition of vegetables to the meal (in this case, white rice) proved to have the most dramatic effect on blood sugar. (1)
Researchers also discovered that the addition of veggies gave a boost to fat-burning hormones.
Hormones That Support Weight Loss
Make one small change to your diet by eating more vegetables today. Vegetables can trigger the release of metabolic hormones to support weight loss and healthy blood sugar levels.
Vegetables trigger the release of key metabolic hormones. These hormones are released in response to the digestive process.
They play an important role in weight loss because they:
- Signal satiety, or fullness
- Control blood sugar
One important hormone is called GLP-1 (or glucagon-like peptide-1).
When it comes to weight loss and metabolic disorders like obesity and type 2 diabetes, GLP-1 is a superhero. It’s the kind of hormone you want to see a lot of. When GLP-1 is out of the picture or when levels are low, it is easier to gain weight. In 2006, researchers at the National Institutes of Health found that the more GLP-1 you have, the more energy you burn while resting. (2)
The movement of sugar into cells also stimulates the release of GLP-1. It’s a vicious cycle since the fat-burning hormone GLP-1 supports blood sugar balance, encouraging the release of insulin and making cells more sensitive to insulin.
This may explain why it is harder for those with type 2 diabetes to shake excess weight.
Indeed, animal studies show lower levels of GLP-1 in those with type 2 diabetes—a situation where cells are resistant to the hormone insulin and sugar is not able to move into cells to be burned as a source of energy. (3)
The Principle of 80/20
The Body Ecology Diet is a strong advocate of the Principle of 80/20. We recommend that:
- 80% of your plate consists of non-starchy vegetables, leafy greens, ocean vegetables, and fermented foods.
- 20% of your plate consists of animal protein, grain-like seeds (such as millet, quinoa, amaranth, and buckwheat), or starchy vegetables.
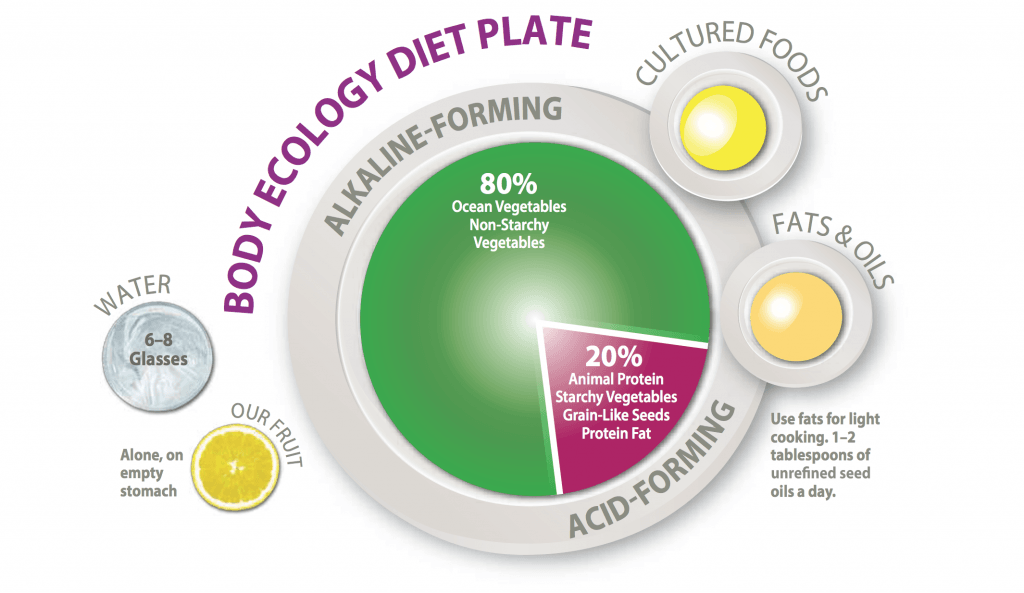
We also recommend that you include a healthy spectrum of fats, like coconut oil, ghee, and olive oil.
A plate full of vegetables works in your favor. The fiber in vegetables feeds the beneficial microbes living in the gastrointestinal tract. These beneficial microbes regulate hormones that support weight loss.
Researchers show that beneficial microbes promote the release of that fat-busting superhero hormone—GLP-1.
In 2013, the National Institutes of Health recommended probiotics as a therapy to fight both obesity and diabetes. They showed that probiotics support high levels of GLP-1, which improves blood sugar, increases satiety, and reduces inflammation in the gut. (4)
One of the best places to get a hearty dose of probiotics is in cultured vegetables and probiotic beverages.
What To Remember Most About This Article:
Though it may seem obvious, new research supports eating more vegetables to effectively lose weight. Vegetables can help stabilize blood sugar and even boost fat-burning hormones.
Eating vegetables can help to signal fullness after a meal and control blood sugar once the GLP-1 hormone is released. Low GLP-1 levels encourage weight gain; GLP-1 can also support balanced blood sugar levels, encourage insulin release, and make cells more sensitive to insulin. This process may explain why it can be difficult for type 2 diabetics to lose weight.
Body Ecology offers the principle of 80/20 for weight loss and blood sugar balance: Eat 80% non-starchy vegetables, leafy greens, ocean vegetables, and fermented foods at each meal, along with 20% animal protein, grain-like seeds, or starchy vegetables. And don’t forget—the National Institutes of Health recommends probiotics to fight off both obesity and diabetes. Try cultured vegetables and probiotic beverages to naturally jumpstart weight loss today.
REFERENCES:
- Kameyama, N., Maruyama, C., Matsui, S., Araki, R., Yamada, Y., & Maruyama, T. (2014). Effects of consumption of main and side dishes with white rice on postprandial glucose, insulin, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1 responses in healthy Japanese men. The British journal of nutrition, 1.
- Pannacciulli, N., Bunt, J. C., Koska, J., Bogardus, C., & Krakoff, J. (2006). Higher fasting plasma concentrations of glucagon-like peptide 1 are associated with higher resting energy expenditure and fat oxidation rates in humans. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 84(3), 556-560.
- Lee, J., Cummings, B. P., Martin, E., Sharp, J. W., Graham, J. L., Stanhope, K. L., … & Raybould, H. E. (2012). Glucose sensing by gut endocrine cells and activation of the vagal afferent pathway is impaired in a rodent model of type 2 diabetes mellitus. American journal of physiology. Regulatory, integrative and comparative physiology, 302(6), R657-66.
- Yadav, H., Lee, J. H., Lloyd, J., Walter, P., & Rane, S. G. (2013). Beneficial Metabolic Effects of a Probiotic via Butyrate-induced GLP-1 Hormone Secretion. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 288(35), 25088-25097.









